

If the two letters fall in the same column of the matrix, you substitute them with the next letter in the column (going down).The next letter of the last in a row is the first letter in that row. If the two letters fall in the same row of the matrix, you substitute them with the next letter in the row.When you get two letters, if they are the same letter, you add a “filler” in the middle.We encrypt the message using two letters each time.Letters are placed only once in the matrix.

you start filling the matrix with the key, then you use the alphabet. In this matrix, I and J are in the same cell.

We will use C++ to write this algorithm due to the standard template library support. The original message and the encrypted message will be: original message: he lx ow or ld We will generate the following table: t e s a b
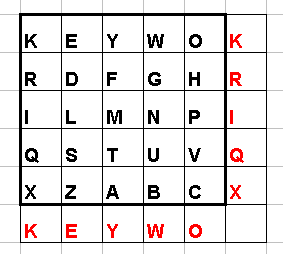
If the pairs are (x1,y) and (x2,y), then we choose the letters at (x1+1,y) and (x2+1,y).įor example, if the message is “helloworld” and the key is “test”. If the pairs are (x,y1) and (x,y2), then we choose the letters at (x,y1+1) and (x,y2+1). Suppose the pair is XY and X is at position (x1,y1) and Y is at position (x2,y2), we choose the letters which are at position (x2,y1) and (x1,y2). Then for each pair, we look up the position of the letters in the table. After the table is generated, we divide the message into the pairs of 2. We usually omit the letter i or j so that the number of letters in the table is 25. After this, we fill the table with the remaining letters. To generate the key, we will first fill the table row-wise with the letters of the key. The Playfair cipher uses a 5 by 5 table of letters. The technique encrypts pairs of letters ( bigrams or digrams), instead of single letters as in the simple substitution cipher and rather more complex Vigenère cipher systems then in use. The Playfair cipher is a cryptographic technique that is used to encrypt/decrypt a message. In this post, we will discuss the Playfair Cipher. There are exceptions and some cipher systems may use slightly more, or fewer, characters when output versus the number that was input. In common parlance, “cipher” is synonymous with “ code“, as they are both a set of steps that encrypt a message however, the concepts are distinct in cryptography, especially classical cryptography.Ĭodes generally substitute different length strings of character in the output, while ciphers generally substitute the same number of characters as are input. To encipher or encode is to convert information into cipher or code. An alternative, less common term is encipherment.
#Playfair cipher series#
In cryptography, a cipher (or cypher) is an algorithm for performing encryption or decryption-a series of well-defined steps that can be followed as a procedure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
